Computer Networking, A Top-Down Approach, 5th Edition
Introduction
Elements of a Wireless Networks
- Wireless Hosts: laptop, PDA, IP phone.
- Base Station:
- connected to a wired network.
- relays
- responsible for sending packets between wired network and wireless hosts in its area.
- Wireless Link:
- typically used to connect mobiles to bas stations.
- multiple access protocol coordinates link access.
- Infrastructure Mode:
- handoff: mobile changes base station providing connection into wired network.
- Ad Hoc Mode:
- no base stations.
- nodes can only transmit to other nodes within link coverage.
- nodes organize themselves into a network: route among themselves.
Wireless Network Taxonomy
| Infrastructure | Single Hop | Multiple Hops |
|---|---|---|
| With Infrastructure | Host connects to base station (WiFi, WiMAX, cellular) which connects to larger Internet. | Host relays through several wireless nodes to connect to larger Internet (mesh net). |
| Without Infrastructure | No base station, no connection to larger Internet (e.g., Bluetooth, ad hoc nets). | No base station, no connection to larger Internet. Nodes relay to reach other nodes (e.g., MANET, VANET). |
Wireless Link Characteristics
从下文可以分析出,这里的 link 不能翻译成链路而应该翻译成连接。
- decreased signal strength
- interference from other sources
- multipath propagation
Multiple wireless senders and receivers create additional problems (beyond multiple access): - Hidden Terminal Problem: A and C can not hear each other means A and C are unaware of their interference B.
这里是在讲,A 和 C 因为障碍物的问题而无法直接通信从而无法协调,但他们都能和 B 进行通信,如果 A 和 C 同时向 B 通信会导致冲突。
- SNR (Signal-to-Noise Ratio):
- larger SNR, easier to extract signal from noise.
- increases power \(\to\) increases SNR \(\to\) decreases BER (Bit Error Rate).
- Given SNR, choose physical layer that meets BER requirement, giving highest throughput.
SNR 是信噪比,顾名思义是一个比值,具体计算公式为 \[ \mathrm{SNR} = \frac{P_{\text{signal}}}{P_{\text{noise}}} \] 实际中用单位 db 表示。SNR 越大,说明信号越容易从噪声中分辨出来,通信质量越好。
Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA)
码分多址,这个我们在 data link layer 提到过,类似的有 TDMA 和 FDMA。需要注意的是 CDMA 是一个 physical layer protocol。所以下文用的是 channel 而不是 link。
A kind of channel partitioning protocol.
- Usage: Used in wireless broadcast channels (e.g., cellular, satellite).
- Code Assignment: Each user is assigned a unique “code” (code set partitioning).
- Frequency Sharing: All users share the same frequency but use distinct “chipping” sequences to encode data.
- Signal Encoding:
- Encoded signal = (original data) (chipping sequence).
- Signal Decoding:
- Decoding is done using the inner product of the encoded signal and the chipping sequence.
- Advantage: Allows multiple users to coexist and transmit simultaneously with minimal interference (if codes are orthogonal). > 这里提到的 unique code 和 chipping sequence 是同一个事物。
CDMA Encode/Decode Process
Sender:
- Data Encoding:
- Each sender has a unique code (chipping sequence)
c_m. - Encoded signal for each data bit:
\[ Z_{i,m} = d_i \cdot c_m \]d_i: Original data bit.c_m: Chipping sequence.
- Each sender has a unique code (chipping sequence)
- Channel Output:
- Encoded signals are transmitted over the shared channel.
- Channel output combines signals from all senders.
Receiver:
- Signal Decoding:
- Receiver uses the inner product of the received signal and its own chipping sequence to decode data: \[ D_i = \frac{\sum_{m=1}^{M} Z_{i,m} \cdot c_m}{M} \]
D_i: Decoded data bit.Z_{i,m}: Received signal.c_m: Receiver’s chipping sequence.
- Receiver uses the inner product of the received signal and its own chipping sequence to decode data: \[ D_i = \frac{\sum_{m=1}^{M} Z_{i,m} \cdot c_m}{M} \]
- Output:
- Decoded data bits are extracted from the combined channel output.
每个发送端都被分配一个唯一的码字(chipping sequence),码字的长度应该足够长,按理来讲,如果有 \(N\) 个用户,码字长度 \(M \geq N\)。码字具体为:用 \(+1\) 和 \(-1\) 分别代表 \(1\) 和 \(0\)。发送者将发送数据与码字相乘,这里指的是位对码字相乘。发送后数据会和其他所有发送者的信息在 channel 中叠加。解码公式有一个前提:要求 user 使用的码字之间正交。除以 M 是为保证归一化。
还要补充的是,CDMA 的核心思想是:所有用户在 same frequency 和 same time 的情况下发送信息。此时应用 CDMA。如果 frequency 不一致,也不会发生信号叠加,此时应该用 FDMA。
WiFi: 802.11 Wireless LANs
前部分介绍了 wireless link 及其用到的 CDMA protocol,
- all use CSMA/CA for multiple access. > data link layer 部分我们讲过了 CSMA/CD。
- all have base-station and ad-hoc network versions.
The 802.11 LAN Architecture
- wireless host communicates with base station (base station = access point (AP))
- Basic Service Set (BSS) (aka “cell”一片区域) in infrastructure mode contains:
- wireless hosts
- access point (AP): base station
- ad hoc mode: hosts only
- 层次关系:一个 subnet 可以包含多个 BSS,多个无线主机通过不同接入点接入同一子网
- 切换过程:
- 当移动设备在同一子网内的不同 BSS 之间移动时,只需改变 BSS 关联(链路层切换),IP 地址保持不变
- 当移动设备跨子网移动时,除了需要切换 BSS,还需要获取新子网的 IP 地址(通常通过 DHCP)
- 地址分配:BSS 关注 MAC 地址,而 Subnet 关注 IP 地址
- 管理机制:BSS 由 AP 管理,Subnet 由路由器管理
| 特性 | BSS | Subnet |
|---|---|---|
| 所属网络层次 | 物理层和数据链路层 (OSI 第 1、2 层) | 网络层 (OSI 第 3 层) |
| 定义标准 | IEEE 802.11 标准 | IP 协议标准 |
| 标识符 | BSSID (MAC 地址) | IP 地址前缀和子网掩码 |
| 地址范围 | 单个无线接入点覆盖范围 | 可跨多个接入点,由路由器定义 |
| 关注点 | 无线媒体访问和信号传输 | IP 数据包的寻址和路由 |
| 设备组织方式 | 围绕单个接入点的无线主机集合 | 共享同一网络前缀的主机集合 |
| 移动特性 | 设备在 BSS 间移动需要进行切换 (handoff) | 在同一子网内的移动不需要更改 IP 地址 |
802.11: Channels, Association
- Frequency Spectrum: 2.4GHz-2.485GHz (802.11b) divided into 11 channels.
- AP Configuration: Admin selects frequency for AP; interference may occur if neighboring APs use the same channel.
- Host Association:
- Scans channels for beacon frames with AP’s SSID and MAC address.
- Selects an AP to associate with.
- May perform authentication.
- Typically runs DHCP to obtain an IP address in the AP’s subnet. > 前文我们讲 CDMA 的时候提到了: CDMA 的所有用户使用相同的 frequency。通常情况下,一个 AP 在同一时刻只工作在一个信道(即一个频率范围),只能收发该信道上的无线信号。
802.11: Passive/Active Scanning
Beacon Frame(信标帧) 是 IEEE 802.11 无线局域网(WiFi)协议中由接入点(AP, Access Point)周期性广播的一种管理帧。
- Passive Scanning:
- APs send beacon frames.
- Host (H1) sends Association Request frame to selected AP.
- Selected AP sends Association Response frame to H1.
- Active Scanning:
- Host (H1) broadcasts Probe Request frame.
- APs respond with Probe Response frames.
- Host (H1) sends Association Request frame to selected AP.
- Selected AP sends Association Response frame to H1.
这两种方式最后两步都是一样的。
IEEE 802.11: Multiple Access
data link layer
Collision Avoidance in 802.11
- Problem: Collisions occur when \(2\) more nodes transmit simultaneously.
- Solution:
- CSMA: Sense the channel before transmitting to avoid collisions with ongoing transmissions.
- No Collision Detection:
- Difficult to sense collisions while transmitting due to weak received signals (fading).
- Hidden terminal and fading issues prevent sensing all collisions.
- Goal: Use CSMA/CA (Collision Avoidance) to minimize collisions.
IEEE 802.11 MAC Protocol: CSMA/CA
DIFS 是分布式帧间间隔(Distributed Inter-Frame Space)的缩写。SIFS 是短帧间间隔(Short Inter-Frame Space)的缩写。Link(链路):在有线网络中,通常指两个节点之间的物理连接。Channel(信道):在无线网络中,指的是一段特定频率范围内的无线传输资源,多个节点可以共享同一个信道。
802.11 Sender
- Channel Idle:
- If the channel is idle for DIFS, transmit the entire frame (no collision detection).
- Channel Busy:
- Start a random backoff timer.
- Timer counts down while the channel is idle.
- Transmit when the timer expires.
- If no ACK is received, increase the random backoff interval and repeat step \(2\).
802.11 Receiver
- If the frame is received correctly:
- Return an ACK after SIFS (ACK is needed to address the hidden terminal problem).
Avoiding Collisions: RTS/CTS Mechanism
- Idea: Allow sender to reserve the channel to avoid collisions of long data frames.
- Process:
- Sender transmits a small Request-to-Send (RTS) packet to the base station (BS) using CSMA.
- RTS packets may collide, but they are short.
- BS responds with a Clear-to-Send (CTS) packet, broadcast to all nodes.
- Sender transmits the data frame.
- Other stations defer their transmissions upon hearing the CTS.
- Advantage: Completely avoids collisions of long data frames by using small reservation packets.
- 发送预约请求(RTS)
- 发送方先发送一个很短的 RTS(Request to Send)帧给基站(或接入点,AP),请求占用信道。
- 接收预约确认(CTS)
- 基站收到 RTS 后,如果信道空闲,则广播一个 CTS(Clear to Send)帧,通知所有节点允许该发送方发送数据。
- 数据发送
- 发送方收到 CTS 后,立即发送长数据帧。
- 其他节点监听
- 网络中其他节点收到 CTS 后,会在指定时间内暂停发送,避免与当前数据帧发生冲突。
802.11 Addressing
下表总结了 802.11 帧的各字段及其作用:
| 字段名 | 长度(字节) | 作用说明 |
|---|---|---|
| frame control | 2 | 帧控制字段,指示帧类型、控制信息等 |
| duration | 2 | 持续时间字段,指示信道预留时间 |
| address 1 | 6 | 接收方 MAC 地址(无线主机或 AP) |
| address 2 | 6 | 发送方 MAC 地址(无线主机或 AP) |
| address 3 | 6 | 路由器接口的 MAC 地址(AP 所连接的路由器接口) |
| seq control | 2 | 序列控制字段,帧编号等 |
| address 4 | 6 | 仅在 ad hoc 模式下使用的地址 |
| payload | 0 - 2312 | 数据负载部分 |
| CRC | 4 | 循环冗余校验,用于差错检测 |
说明: - address 1:接收方 MAC 地址 - address 2:发送方 MAC 地址 - address 3:AP 所连接的路由器接口的 MAC 地址 - address 4:仅 ad hoc 模式下使用
Mobility within Same Subnet
Host 在统一子网下不同 BSS 移动,switch 如何得知 host 当前在哪个 BSS 内?实际上 switch 能通过 self-learning:switch will see frame from H1 and remember which switch port can be used to reach H1。
Power Management
- 定时唤醒机制:
休眠节点在进入省电模式(Power Save Mode)时,会本地保存下一个 beacon frame 的预计到达时间,并设置定时器(timer)。 - 硬件支持:
无线网卡硬件通常具备低功耗计时功能,可以在主机休眠时保持计时,确保在 beacon frame 到来前自动唤醒。 - 唤醒流程:
节点休眠后,定时器到达设定时间,节点自动唤醒,监听并接收 AP 广播的 beacon frame,判断是否有待接收的数据。 - 节能的核心在于节点休眠:
节能的关键不是 AP 是否省电,而是无线终端(如手机、笔记本)可以长时间休眠,仅在 beacon frame 到来时短暂唤醒,大大减少无线网卡的活跃时间和能耗。 - AP 通常为插电设备:
AP 持续广播 beacon frame 对其本身能耗影响不大,因为 AP 通常是接入电源的设备,不依赖电池。 - 终端省电效果显著:
终端设备在无数据通信时可以关闭大部分无线模块,仅保留低功耗计时和唤醒功能,只有在需要接收数据或发送数据时才唤醒主模块,极大延长了电池续航。
802.15: Personal Area Network
个人热点。使用 ad hoc mode,参考 bluetooth protocol。
802.16: WiMAX
Cellular Internet Access
介绍几个概念: - Cell:一个区域,里面有一个 base station,mobile users 通过这个基站连接到 network。 - MCS:Mobile Switching Center。连接 base station 和 wired network。
The First Hop
第一跳为 users 到 base station。显然是一个 multiple senders 的场景,可以用 FDMA、TDMA 和 CDMA 分离数据。
Cellular standards: brief survey
2G Systems
- Voice Channels:
- IS-136 TDMA: Combined FDMA/TDMA (North America).
- GSM: Global System for Mobile Communications, combined FDMA/TDMA (most widely deployed).
- IS-95 CDMA: Code Division Multiple Access.
2.5G Systems
- Voice and Data Channels:
- GPRS: Evolved from GSM, data sent on multiple channels.
- EDGE: Enhanced modulation, data rates up to 384K.
- CDMA-2000 (Phase 1): Data rates up to 144K, evolved from IS-95.
3G Systems
- Voice/Data:
- UMTS: High-Speed Uplink/Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA/HSUPA), 3 Mbps.
- CDMA-2000: Data service (1xEVDO), up to 14 Mbps.
4G Systems
- Voice/Data:
- LTE: Employs OFDM and MIMO techniques, 100 Mbps for downlink, 50 Mbps for uplink.
Principles: Addressing and Routing to Mobile Users
mobile user, passing through multiple access point while maintaining ongoing connections (like cell phone)
Mobility: Vocabulary
Home Network
- Permanent “home” of the mobile device (e.g., 128.119.40/24).
- Permanent Address: Address in the home network, always used to reach the mobile (e.g., 128.119.40.186).
- Home Agent: Entity in the home network that performs mobility functions for the mobile when it is remote.
Visited Network
- Network where the mobile device currently resides (e.g., 79.129.13/24).
- Care-of-Address: Temporary address assigned to the mobile in the visited network (e.g., 79.129.13.2).
- Foreign Agent: Entity in the visited network that performs mobility functions on behalf of the mobile.
Correspondent
- The entity that wants to communicate with the mobile device.
Consider friend frequently changing addresses, how do you find her?
let end-systems handle it: - indirect routing: communication from correspondent to mobile goes through home agent, then forwarded to remote - direct routing: correspondent gets foreign address of mobile, sends directly to mobile
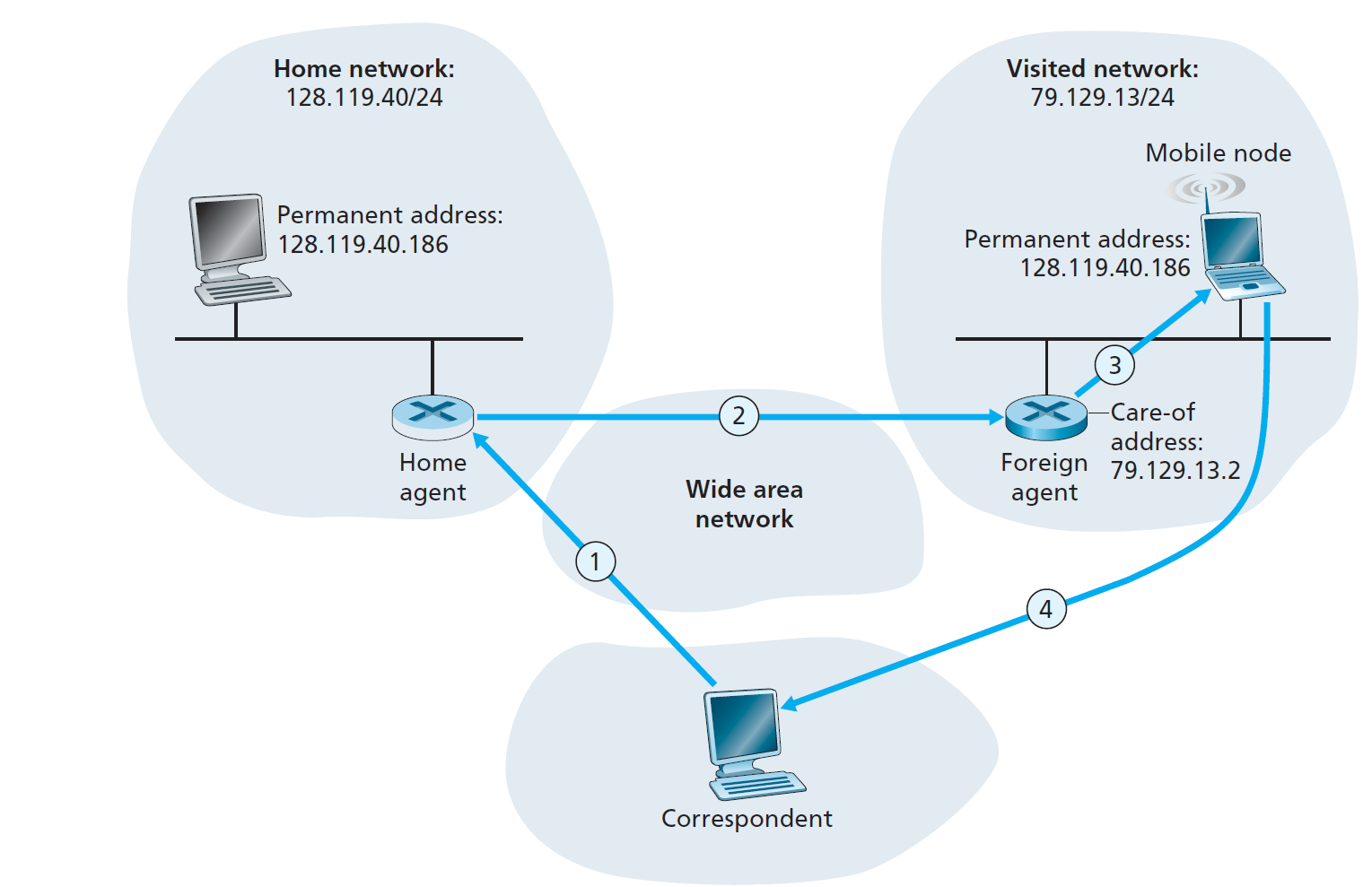
第一种 indirect routing,见上图所示,当你的朋友移动到其它 foreign 网络,他会得到一个 Care-of-Address,这个地址是临时的,用于在当前所在子网下通信,但他有一个 Permanent Address,可以通过联系他的 Home agent,从而联系到他所在子网的 Foreign agent,从而联系到他。
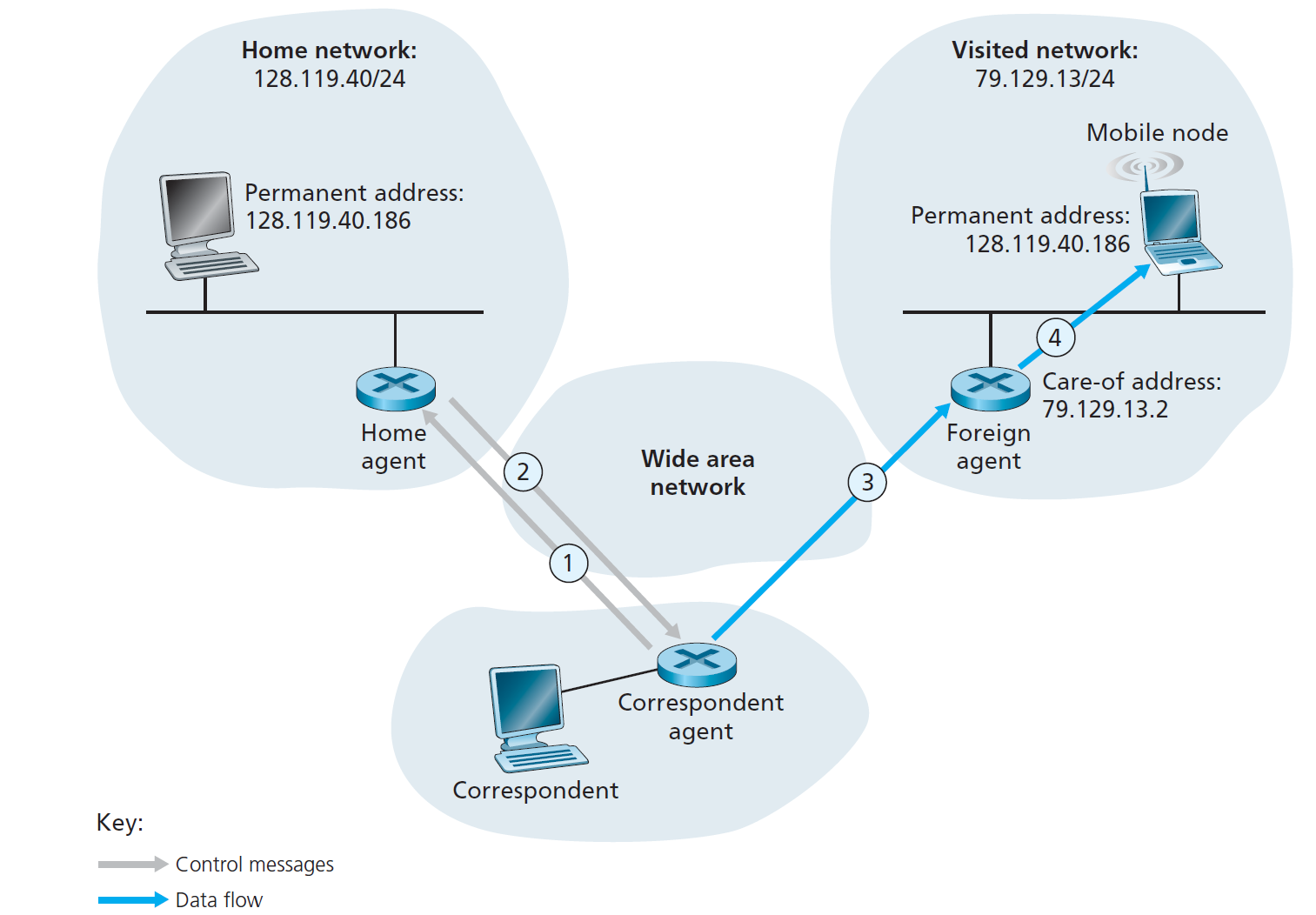
第二种是 direct routing,这种是先通过联系他的 Home agent,得到他所在子网的 IP address,从联系到他。
需要补充两点: 1. correspondent 如何得到 friend 的 permanent address. - permanent address(永久地址) 是 friend 在 home network 的固定 IP 地址,通常是 friend 在 home network 注册时分配的。 - correspondent(通信对端) 想要联系 friend 时,通常会通过 DNS 查询等方式获得 friend 的 permanent address(即 home address)。 - 这个 permanent address 是公开的、长期有效的,类似于家庭住址,所有通信发起者都可以通过标准方式获得。 2. home agent 如何维护 friend 所在子网的 agent 和 IP address. - home agent(归属代理) 是部署在 friend 的 home network 内的一个特殊节点,负责跟踪 friend 的当前位置。 - 当 friend 移动到新的 visited network 并获得新的 care-of address 时,会向 home agent 注册自己的新位置(即 care-of address 和 foreign agent 的信息)。 - home agent 会维护一个映射表,记录每个移动节点的 permanent address 与其当前的 care-of address(以及 foreign agent 的信息,如果有)。 - 当有数据包发往 friend 的 permanent address 时,home agent 会将这些数据包隧道转发(tunnel)到 friend 当前的 care-of address(即 friend 所在子网的 foreign agent 或直接到 friend 本身)。
Mobile IP: agent discovery
Agent advertisement: foreign/home agents advertise service by broadcasting ICMP messages (typefield = 9)
End-of-chapter exercises
R.1
Question and Answer:
What does it mean for a wireless network to be operating in “infrastructure mode”? If the network is not in infrastructure mode, what mode of operation is it in, and what is the different between that mode of operation and infrastructure mode?
在无线网络中,“基础设施模式”(infrastructure mode)指的是网络中存在一个基站(如接入点,AP),无线主机通过基站连接到有线网络或更大的互联网。在这种模式下,基站负责在无线主机和有线网络之间中继数据。如果网络不处于基础设施模式,则它处于“自组织模式”(ad hoc mode)。在自组织模式中,没有基站,节点只能与其链路覆盖范围内的其他节点通信,节点之间通过自组织的方式形成网络并相互路由。两者的主要区别在于是否依赖基站:基础设施模式依赖基站,而自组织模式则完全由节点自主协作。
R.2
Question and Answer:
What are the four type of wireless networks identified in our taxonomy in Section \(6.1\)? Which of these types of wireless networks have you used?
Section \(6.1\) 中提到的 \(4\) 种无线网络结构如下:| Infrastructure | Single Hop | Multiple Hops |
|---|---|---|
| With Infrastructure | Host connects to base station (WiFi, WiMAX, cellular) which connects to larger Internet. | Host relays through several wireless nodes to connect to larger Internet (mesh net). |
| Without Infrastructure | No base station, no connection to larger Internet (e.g., Bluetooth, ad hoc nets). | No base station, no connection to larger Internet. Nodes relay to reach other nodes (e.g., MANET, VANET). |
其中像 WiFi 和 Bluetooth 经常使用。
R.3
Question and Answer:
What are the differences between the following types of wireless channel impairments: path loss, multipath propagation, interference from other sources?
下面是对三种信道损伤的解释:| 损伤类型 | 详细解释 |
|---|---|
| 路径损耗 (path loss) | 信号随传播距离增加而自然衰减的现象。遵循平方反比或更高次幂衰减规律,与距离和频率相关。主要包括自由空间损耗、大气吸收、障碍物衰减等,是无线通信中的基础衰减现象。 |
| 多径传播 (multipath propagation) | 信号通过多个不同路径同时到达接收器的现象。由信号在建筑物、地面等物体表面的反射、散射、折射和绕射导致。产生相位差异使信号彼此增强或抵消,造成信号衰落、时延扩展和符号间干扰。 |
| 外部干扰 (interference from other sources) | 来自其他发射源的电磁波对当前通信的干扰。包括同频干扰(相同频道上的其他发射器)、相邻频道干扰和电子设备噪声等。干扰与当前信号混合,降低信噪比和通信质量。 |
R.4
Question and Answer:
As a mobile node gets farther and farther away from a base station, what are two actions that a base station could take to ensure that the loss probability of a transmitted frame does not increase?
- Wireless Link Characteristics 部分提到:
- SNR (Signal-to-Noise Ratio):增大信号强度可以提高信噪比,从而降低误码率(BER)。
- decreased signal strength:信号强度的降低会影响通信质量。
- IEEE 802.11 MAC Protocol: CSMA/CA 部分提到:
- Collision Avoidance:通过避免冲突来提高传输成功率。
- Cellular Internet Access 部分提到:
- LTE 使用了 OFDM 和 MIMO 技术,这些技术可以提高信号覆盖范围和传输效率。
结合这些内容,可以得出以下两种可能的措施: - 增大发射功率:提高信号强度以补偿路径损耗。 - 使用多天线技术(如 MIMO):通过空间分集技术提高信号质量和覆盖范围。
R.10
Question and Answer:
Suppose the IEEE \(802.11\) RTS and CTS frames were as long as the standard DATA and ACK frames. Would there be any advantage to using the CTS and RTS frames? Why or why not?
- Avoiding Collisions: RTS/CTS Mechanism 部分提到:
- RTS 和 CTS 的主要作用是 避免长数据帧的冲突。
- RTS 和 CTS 包较小,即使发生冲突,影响也较小。
- 使用 RTS/CTS 机制可以通过小型的预留包来减少长数据帧的冲突。
- 如果 RTS 和 CTS 包与标准的 DATA 和 ACK 包一样长,那么它们的优势将丧失,因为:
- 冲突成本增加:长 RTS 和 CTS 包的冲突会导致更大的资源浪费。
- 效率降低:长 RTS 和 CTS 包会增加额外的开销,降低整体网络效率。
R.16
Question and Answer:
If a node has a wireless connection to the Internet, does that node have to be mobile? Explain. Suppose that a user with a laptop walks around her house with her laptop, and always accesses the Internet through the same access point. Is this user mobile from a network standpoint? Explain.
一个节点拥有无线连接,并不意味着它是移动的。无线连接只是物理层和链路层的接入方式,只要设备通过无线方式接入网络,无论它是否实际移动,都可以称为无线节点,但不一定是移动节点。用户在家中携带笔记本,始终通过同一个 AP 上网,这说明用户始终在同一个 subnet 和 BSS 内,所以不认为用户发生了网络层的移动。
R.17
Question and Answer:
What is the difference between a permanent address and a care-of address? Who assigns a care-of address?
- permanent address(永久地址)
- 也称为 home address(归属地址),是移动节点在其归属网络(home network)中的固定 IP 地址。
- 这个地址在移动节点无论身处何地都不会改变,始终用于标识该节点的身份。
- 例如:移动节点在家乡网络的 IP 地址 128.119.40.186。
- care-of address(临时地址)
- 是移动节点在访问网络(visited network)中临时获得的 IP 地址。
- 当移动节点离开归属网络,进入其他网络时,会在该访问网络中分配一个新的 IP 地址,这个地址用于在当前网络中进行通信。
- 例如:移动节点在外地网络获得的 IP 地址 79.129.13.2。
- care-of address 通常由访问网络 visited network 分配,具体来说:
- 可以由访问网络中的外部代理 Foreign Agent 分配;
- 也可以通过 DHCP 等自动分配协议由访问网络的路由器分配。
R.19
Question and Answer:
What are the purposes of the HLR and VLR in GSM networks? What elements of mobile IP are similar to the HLR and VLR?
| GSM 网络 | Mobile IP 协议 | 主要作用 |
|---|---|---|
| HLR | Home Agent | 记录永久信息和当前位置 |
| VLR | Foreign Agent | 临时管理当前区域内的用户/节点信息 |
P.5
Question and Answer:
Suppose there are two ISPs providing WiFi access in a particular café, with each ISP operating its own AP and having its own IP address block. a. Further suppose that by accident, each ISP has configured its AP to operate over channel 11. Will the 802.11 protocol completely break down in this situation? Discuss what happens when two stations, each associated with a different ISP, attempt to transmit at the same time. b. Now suppose that one AP operates over channel 1 and the other over channel 11. How do your answers change?
a.:802.11 协议不会完全失效,但两个 AP 及其关联的 hosts 会在 physical layer 竞争同一个信道的使用权。如果两个 hosts 同时发送数据,此时会产生 collision,尽管 CSMA/CA 协议会尽可能避免冲突,但由于信号干扰,冲突仍会发生,导致通信变得不稳定。
b.:此时两个 AP 用不同的信道,互不干扰,通信正常。
P.13
Question and Answer:
In mobile IP, what effect will mobility have on end-to-end delays of datagrams between the source and destination?
- 间接路由(Indirect Routing)增加路径长度
- 在移动 IP 的典型实现中,数据报首先被发送到移动节点的 home agent(归属代理),然后由 home agent 转发(隧道)到移动节点当前的 care-of address(临时地址)。
- 这种绕路导致数据报的实际传输路径比直接路由更长,增加了端到端延迟。
- 例如,源主机 → home agent → foreign agent → 移动节点。
- 切换期间的延迟抖动
- 当移动节点从一个网络切换到另一个网络时(如切换 AP 或基站),需要重新获取 care-of address 并向 home agent 注册新位置。
- 在切换和注册期间,可能会出现短暂的不可达或数据包丢失,导致延迟波动或瞬时增加。
- 三角路由问题
- 在 indirect routing 下,通信对端(correspondent)始终将数据包发往 permanent address,导致所有流量都要经过 home agent,形成所谓的三角路由。
- 这进一步增加了端到端的传输时延,尤其当 home agent 距离通信双方较远时影响更明显。
- 优化路由(Direct Routing)可减少延迟
- 如果采用 direct routing(如移动节点的当前位置被通知给通信对端),数据报可以直接从源主机发往移动节点当前的 care-of address,端到端延迟会降低。
- 但 direct routing 需要额外的机制来保证安全和地址同步。