支持向量机
Linear SVM in Linearly Separable Case
Define Training Data
Define Separating Hyperplane
Define Classification Decision Function
Define Functional Margin
Define Geometric Margin
$\lVert w \rVert$ is $L_2$ norm
What’s More
Maximize Margin
Originally, we solve the following question.
We can transform this into a convex quadratic programming problem.
Support Vector
Margin
Learning Algorithm
- input: $T$
output: Separating Hyperplane and $f(x)$
Solve and get the optimal solution $\alpha^*$.
- Calculate.
Linear SVM
Learning Algorithm
- input: $T$
output: Separating Hyperplane and $f(x)$
Solve and get the optimal solution $\alpha^*$.
- Calculate.
Hinge Loss Functional
Non-linear SVM
Kernel Trick
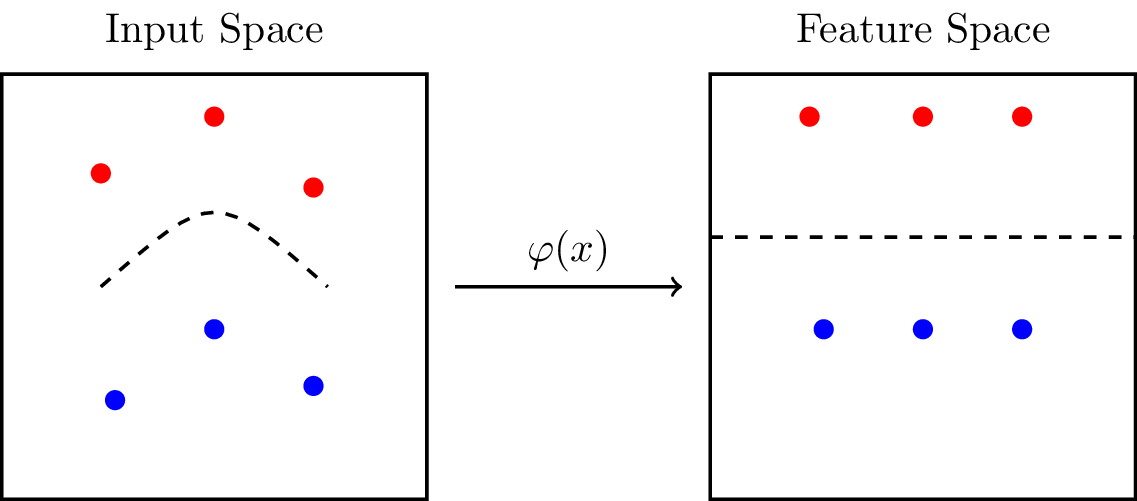
Positive Definite Kernel Function
$K :\mathcal{X} \times \mathcal{X} \to \mathbb{R}$ is a symmetric function, $K(x, z)$ is positive definite kernel function $\Leftrightarrow$ $\forall x_i \in \mathcal{X}, \quad i = 1, 2, 3, \dots, m, \quad \text{the gram matrix corresponding ot } K(x, z) \text{is positive semi-definite.}$
Gram Matrix
Learning Algorithm
- input: $T$
output: Separating Hyperplane and $f(x)$
Solve and get the optimal solution $\alpha^*$.
- Calculate.
SMO Algorithm
Algorithm concept
SMO algorithm is a kind of heuristic algorithm.
Solution methods for quadratic programming with two variables
We choose $\alpha_1, \alpha_2$, fixing other variables $\alpha_i (i = 3, 4, \dots, N)$.
Now, we solve following question:
$K_{ij} = K(x_i, x_j),i,j = 1,2, \dots, N$, $\zeta$ is a constant, the constant term in $(2)$ is omitted.
We consider best optimal question about $\alpha_2$.
if $ y_1 \neq y_2 $.
else.
Now, we update $\alpha_2$.
Next, update $\alpha_1$.
Solution methods for selecting variables
- select the highest $E_i$ in all nodes as $\alpha_1$.
- select the highest $|E_1 - E_2|$as $\alpha_2$.
Solution methods for calculating threshold b and E
What’s more
updating $E$.
$\mathcal{S}$ includes all SV $x_i$.